By: Catherine Graham

Jeremy D. Brown named Sloan Research Fellow
- February 15, 2022
- Center NewsRobotics, Augmented Reality, and Devices
Jeremy D. Brown is among 118 Sloan Research Fellows honored for their exceptional early-career science research.
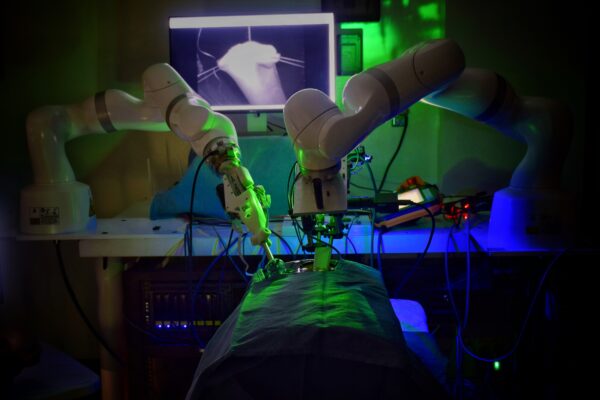
Robot performs first laparoscopic surgery without human help
- January 27, 2022
- Robotics, Augmented Reality, and Devices
In four experiments on pig tissues, the robot excelled at suturing two ends of intestine—one of the most intricate and delicate tasks in abdominal surgery.

New $20 million grant will help Johns Hopkins develop technologies for healthy aging
- November 16, 2021
- Center NewsMachine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
Multicenter collaboration will focus on the use of artificial intelligence to improve long-term health, independence for older people.

Announcing new Seed Grant Awards
- November 9, 2021
- Center News
The new grants will fund engineering innovations that aim to: introduce next generation assistive robots for children with autism spectrum disorder; advance shared-control strategies for skills assessment in robotic surgery; a develop artificial-intelligence based tools to evaluate therapies for vascular anomalies
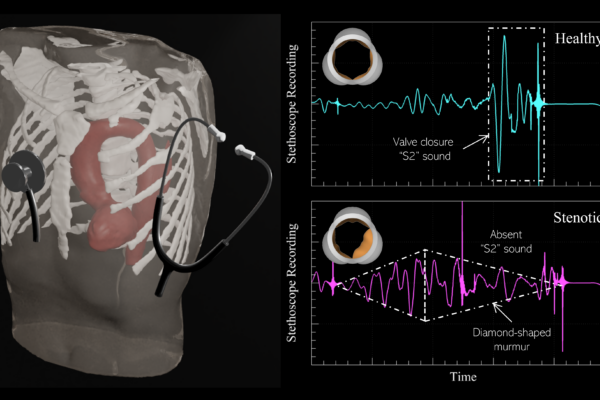
Computer-assisted auscultation proves effective at detecting early-stage heart disease
- October 27, 2021
- Uncategorized
Johns Hopkins mechanical engineers have developed an algorithm that “listens” to heart sound recordings and detects heart disease with an accuracy that is similar to that of expert cardiologists.
A new approach to mapping the brain could make surgery safer
- October 26, 2021
- Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
Doctoral student Naresh Nandakumar is developing a painless, non-invasive approach using functional magnetic resonance imaging, or fMRI, to locate the eloquent cortex.