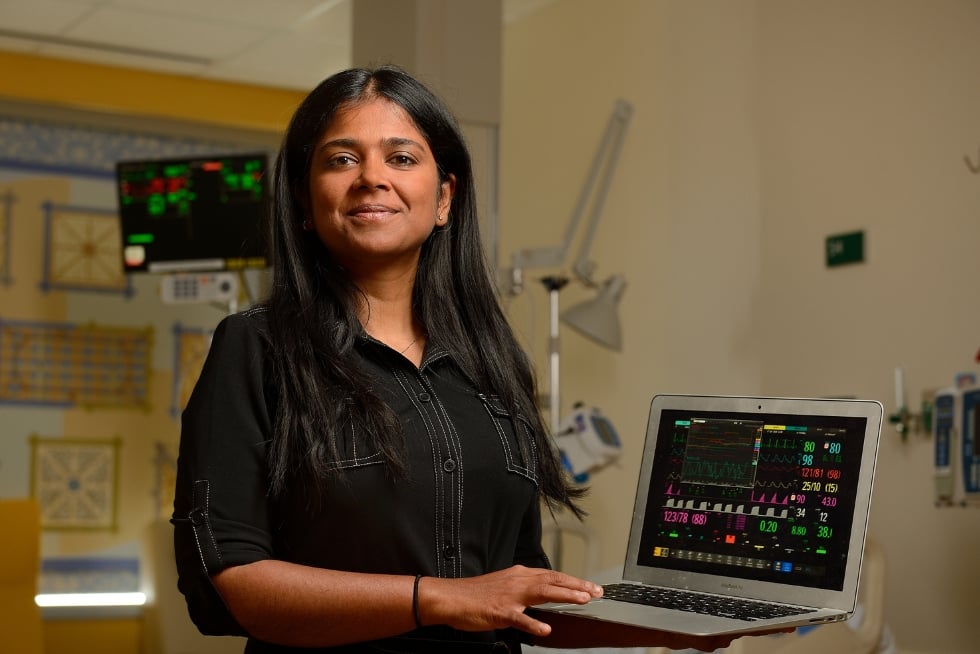
National Science Foundation funding helped Suchi Saria develop and launch a lifesaving early warning system that uses artificial intelligence to... Read More
Researchers
Richard Day
Related Projects
Data Science for AI in Healthcare: An Online Course
Machine learning (ML) & artificial intelligence (AI) frameworks are expected to play a significant role in driving innovation and discovery in healthcare research. Examples of ML & AI applications in health care include medical imaging and diagnostics, robot-assisted surgeries, and remote care assistance. To foster research collaborations using ML & AI,...
Noninvasive Localization of Epileptic Seizures
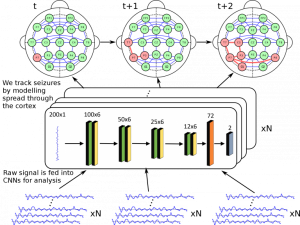 Epilepsy affects nearly 3.5 million people in the United States and is linked to a five-fold increase in mortality. While epilepsy is often controlled with medication, 20-40% of patients are medically refractory and continue to experience seizures in spite of drug therapies. The alternative for...
Epilepsy affects nearly 3.5 million people in the United States and is linked to a five-fold increase in mortality. While epilepsy is often controlled with medication, 20-40% of patients are medically refractory and continue to experience seizures in spite of drug therapies. The alternative for...
Predicting Risk for Glaucoma Progression Based Using AI
Glaucoma is the second leading cause of blindness globally, with approximately 79.6 million people expected to be affected by the disease by 2020. Automated visual field (VF) testing remains the gold standard for identifying patients with glaucoma and judging worsening of disease. Approximately 5% of patients with glaucoma undergo rapid worsening of their VF test.
Radiology AI Lab (RAIL)
 RAIL is an open structured artificial intelligence focused research collaboration based in the Hopkins Department of Radiology and Radiological Sciences. The group is comprised of physicians and scientists from Johns Hopkins Hospital, the Whiting School of Engineering, and the Applied Physics Laboratory,...
RAIL is an open structured artificial intelligence focused research collaboration based in the Hopkins Department of Radiology and Radiological Sciences. The group is comprised of physicians and scientists from Johns Hopkins Hospital, the Whiting School of Engineering, and the Applied Physics Laboratory,...
Related News
Selected for the Johns Hopkins Institute for Assured Autonomy’s Challenge Grants, their teams are now completing work that began in... Read More
A new study by Hopkins researchers finds that doctors’ diagnostic performance and trust in AI advice depends on how the... Read More
The $1.7 million grant from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation will help the researchers to develop a low-cost point-of-care... Read More